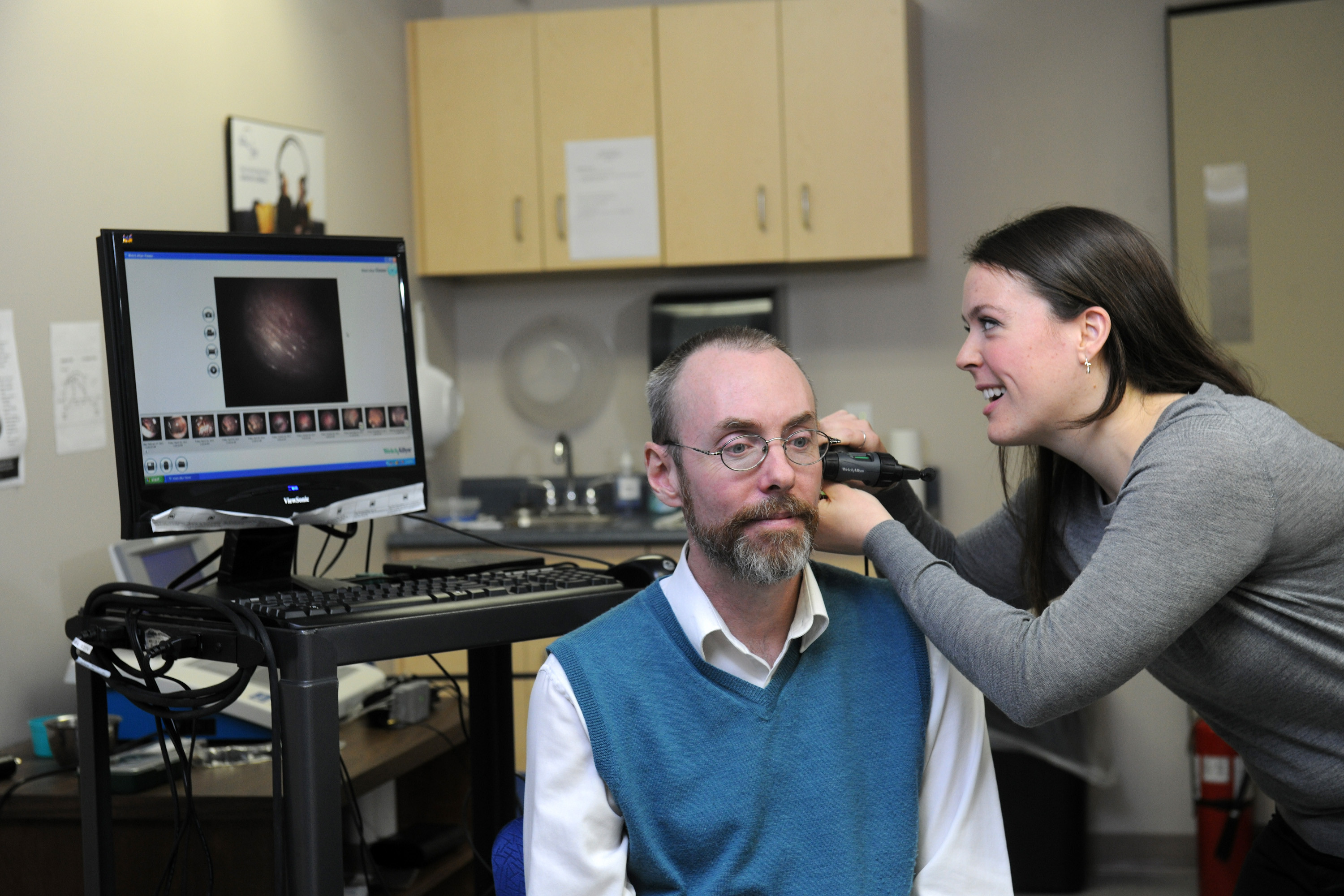
Audiology (MSc)

The audiology program at Dalhousie University involves three years of full-time study allotted to course work, clinical practica, and a research project or thesis. The program leads to a Master of Science (MSc) degree.
Upon completion of the program, students meet the requirements for application for certification by Speech-Language & Audiology Canada (SAC) and for licensure in any of the provinces with government regulation of audiology.
Overview
Audiology Curriculum Map
- Audiology Curriculum Course Connections [PDF - 43kb]
- Foundation Course Linkages [PDF - 82kb]
- Post-foundation Course Topic Summaries [PDF - 66kb]
Course Sequences
Audiologists are health care professionals concerned with the diagnosis, assessment, rehabilitation, and prevention of hearing loss and balance disorders.
More specifically, audiologists:
- perform hearing assessments to determine the degree and type of hearing loss
- administer diagnostic tests to determine the sources and causes of hearing disorder
- use state-of-the-art technology to evaluate and treat hearing loss in children and adults
- fit amplification systems such as hearing aids or cochlear implants
- screen the hearing of newborns
- provide aural rehabilitation to individuals with hearing loss and their families to reduce communication problems and facilitate adjustments to hearing loss
- prevent hearing loss by educating the public and other professionals about the effects of noise on hearing
Career paths
Audiologists often work in collaboration with otolaryngologists, family physicians, nurses, teachers, social workers, psychologists, speech-language pathologists, and other audiologists.
Audiologists work in a variety of environments, including hospitals, community health centres, private clinics, schools, hearing aid manufacturers, and universities.
From a total of 200 professions and jobs, CareerCast.com (2014) ranked Audiologist in the top 10, based on job prospects and income. Chances of employment are enhanced by the willingness of the candidate to relocate.
Go the Links page to obtain more information on hearing science and disorders and on the profession of audiology.
Practicum refers to the development of skills through: the application of academic concepts to the clinical setting, observation of clinical activities, participation in simulated activities, and participation in client care through practicum placements. Students move through these activities in incremental steps, eventually achieving greater responsibility for the care of clients.
First-year audiology students observe clinical activities at the school's in-house audiology clinic. They also participate in a speech-language and hearing screening program of pre-school children at community pre-schools and other facilities.
During second year, audiology students participate in the school’s in-house clinic, known as Sheltered Practicum. Also during this year, students participate in an Observation Practicum, which involves a series of observations of activities such as pediatric assessments, evaluations of clients with auditory processing disorders, ENT surgery, evoked potential testing, hearing aid fitting and others.
During the summer of the second year, students are assigned to facilities on a full-time basis for 12 weeks within the Atlantic Provinces.
In the final externship placement, in the winter term of third year, students are often placed outside of the Halifax area. Students may be placed in sites across Canada and within the United States. Placements outside of Canada will be considered if appropriate clinical supervision is available.
- Canadian Academy of Audiology (CAA)
- Speech-Language & Audiology Canada (SAC)
- Speech and Hearing Association of Nova Scotia (SHANS)
- Sounds+
- American Academy of Audiology (AAA)
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA)
- International Society of Audiology
- Nova Scotia Hearing and Speech Centres (NSHSC)
- Atlantic Provinces Special Education Authority (APSEA)
- Hear-It
- Better Hearing Institute
- Healthy Hearing
- Canadian Hard of Hearing Association
- Canadian Hearing Society
To pursue studies in our Master's programs in Audiology, visit the Admissions section of our website.
Program overview
Overview
Audiology Curriculum Map
- Audiology Curriculum Course Connections [PDF - 43kb]
- Foundation Course Linkages [PDF - 82kb]
- Post-foundation Course Topic Summaries [PDF - 66kb]
Course Sequences
The profession
Audiologists are health care professionals concerned with the diagnosis, assessment, rehabilitation, and prevention of hearing loss and balance disorders.
More specifically, audiologists:
- perform hearing assessments to determine the degree and type of hearing loss
- administer diagnostic tests to determine the sources and causes of hearing disorder
- use state-of-the-art technology to evaluate and treat hearing loss in children and adults
- fit amplification systems such as hearing aids or cochlear implants
- screen the hearing of newborns
- provide aural rehabilitation to individuals with hearing loss and their families to reduce communication problems and facilitate adjustments to hearing loss
- prevent hearing loss by educating the public and other professionals about the effects of noise on hearing
Career paths
Audiologists often work in collaboration with otolaryngologists, family physicians, nurses, teachers, social workers, psychologists, speech-language pathologists, and other audiologists.
Audiologists work in a variety of environments, including hospitals, community health centres, private clinics, schools, hearing aid manufacturers, and universities.
From a total of 200 professions and jobs, CareerCast.com (2014) ranked Audiologist in the top 10, based on job prospects and income. Chances of employment are enhanced by the willingness of the candidate to relocate.
Go the Links page to obtain more information on hearing science and disorders and on the profession of audiology.
Practicum
Practicum refers to the development of skills through: the application of academic concepts to the clinical setting, observation of clinical activities, participation in simulated activities, and participation in client care through practicum placements. Students move through these activities in incremental steps, eventually achieving greater responsibility for the care of clients.
First-year audiology students observe clinical activities at the school's in-house audiology clinic. They also participate in a speech-language and hearing screening program of pre-school children at community pre-schools and other facilities.
During second year, audiology students participate in the school’s in-house clinic, known as Sheltered Practicum. Also during this year, students participate in an Observation Practicum, which involves a series of observations of activities such as pediatric assessments, evaluations of clients with auditory processing disorders, ENT surgery, evoked potential testing, hearing aid fitting and others.
During the summer of the second year, students are assigned to facilities on a full-time basis for 12 weeks within the Atlantic Provinces.
In the final externship placement, in the winter term of third year, students are often placed outside of the Halifax area. Students may be placed in sites across Canada and within the United States. Placements outside of Canada will be considered if appropriate clinical supervision is available.
Links & resources
- Canadian Academy of Audiology (CAA)
- Speech-Language & Audiology Canada (SAC)
- Speech and Hearing Association of Nova Scotia (SHANS)
- Sounds+
- American Academy of Audiology (AAA)
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA)
- International Society of Audiology
- Nova Scotia Hearing and Speech Centres (NSHSC)
- Atlantic Provinces Special Education Authority (APSEA)
- Hear-It
- Better Hearing Institute
- Healthy Hearing
- Canadian Hard of Hearing Association
- Canadian Hearing Society
Apply
To pursue studies in our Master's programs in Audiology, visit the Admissions section of our website.