Examples of Popular A.I. Tools
Many of us have used or interacted with A.I.-driven tools already, examples including product, service, or content suggestions based on our age, gender, or browsing and buying history; captions, transcriptions, and translations; word prediction when we type or text; and more. A.I. is not new, but generative A.I., such as ChatGPT, represents a leap in this kind of technology.
The following are some examples (in alphabetical order) of A.I. tools that may be relevant in your or your students’ work. Please note: Under Nova Scotia privacy law and Dalhousie’s Protection of Personal Information Policy, you are not permitted to require students use a generative A.I. tool or platform for coursework other than the Enterprise version of Copilot [login required], which requires students sign in with their Dalhousie credentials.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a smart chatbot created by OpenAI. It leverages A.I. to engage in human-like conversations with users. It can take what users say or ask, process it, and generate relevant and coherent—albeit not always accurate—responses. It's trained on a vast amount of data from the Internet, allowing it to provide information, answer questions, assist with problem-solving, and offer a wide range of language-based tasks. It “remembers” (and saves) previous conversations which set the context for future interactions.
Visit the ChatGPT website to try it and to learn more.
Example of ChatGPT

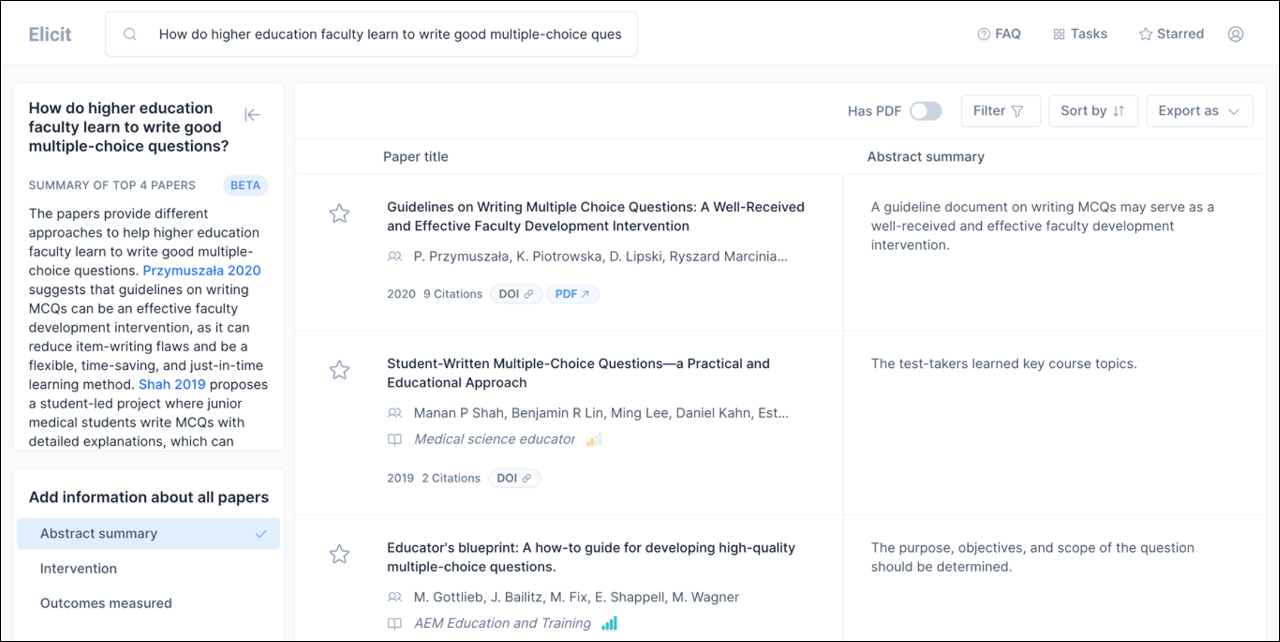
Elicit
This platform is described as a place to help with research. You can submit a research question, and it will respond with a list of published literature that may be relevant to your inquiry. An abstract summary is shown for each result, and the tool allows you to ask follow-up questions about each article. Results can be filtered by keywords, publication date, or study type; results can be sorted by paper title, year of publication, when a PDF of the article is available, and more.
Visit the Elicit website to try it and to learn more.
Example of Elicit
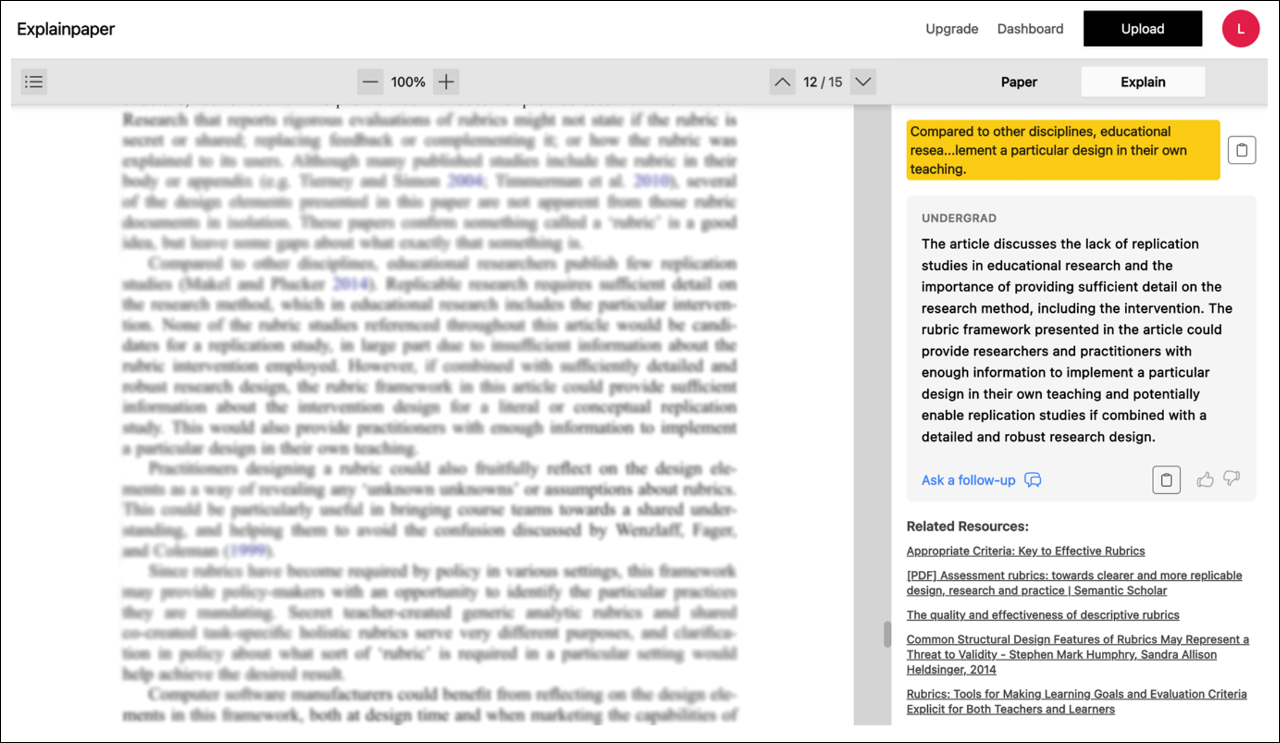
Explainpaper
This A.I. tool can help in summarizing or understanding academic papers. You can upload a paper, highlight a portion of the text, and it will provide you with a simpler explanation of that passage. In a text-based conversation, you can ask the tool to clarify or refine the result. A list of related resources is also shown.
Visit the Explainpaper website to try it and to learn more.
Example of Explainpaper
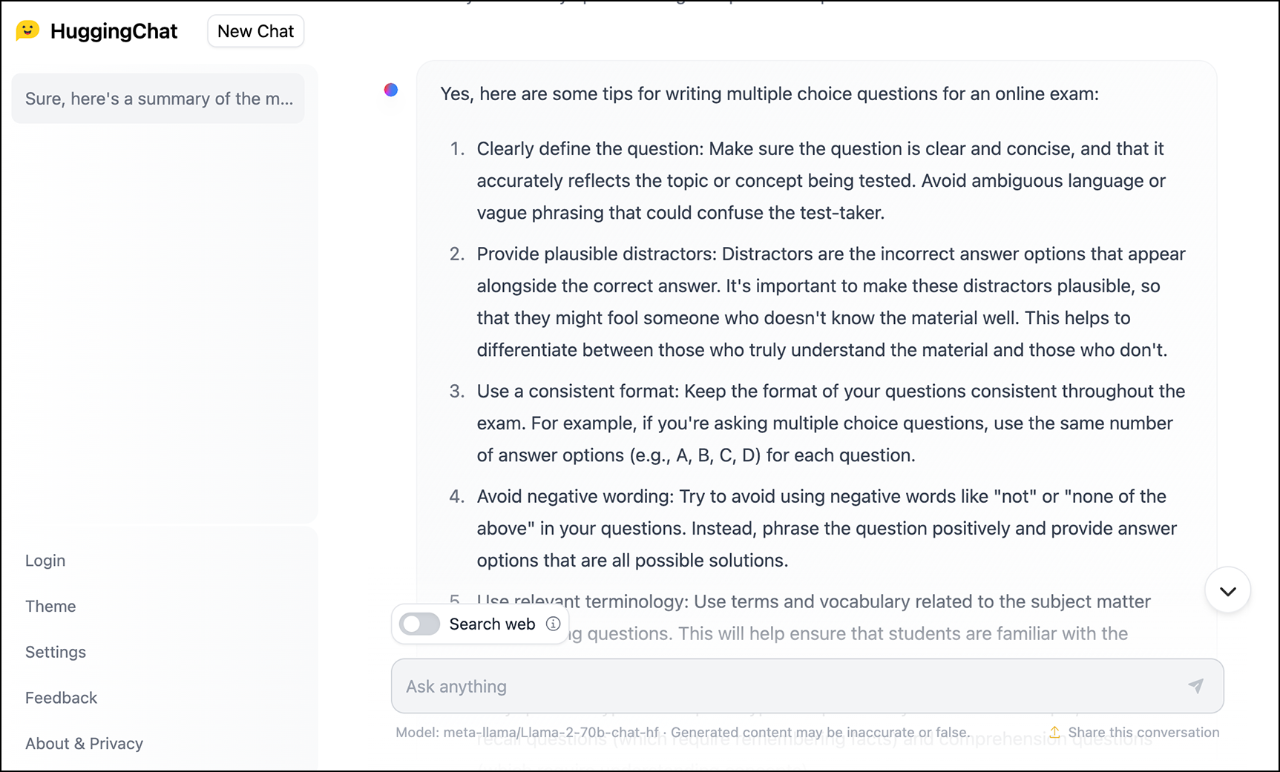
HuggingChat
HuggingChat is an “alternative to ChatGPT” and does not require an account to use. With your prompt, there’s an option to include a web search (although, in testing, there was no difference in response when web search was on or off). Throughout the site, including when you go to create an account, there are warnings that LLM responses may be biased, inaccurate, or false. Also, there is an option to disable data sharing in the app settings.
Visit the HuggingChat website to try it and to learn more.
Example of HuggingChat
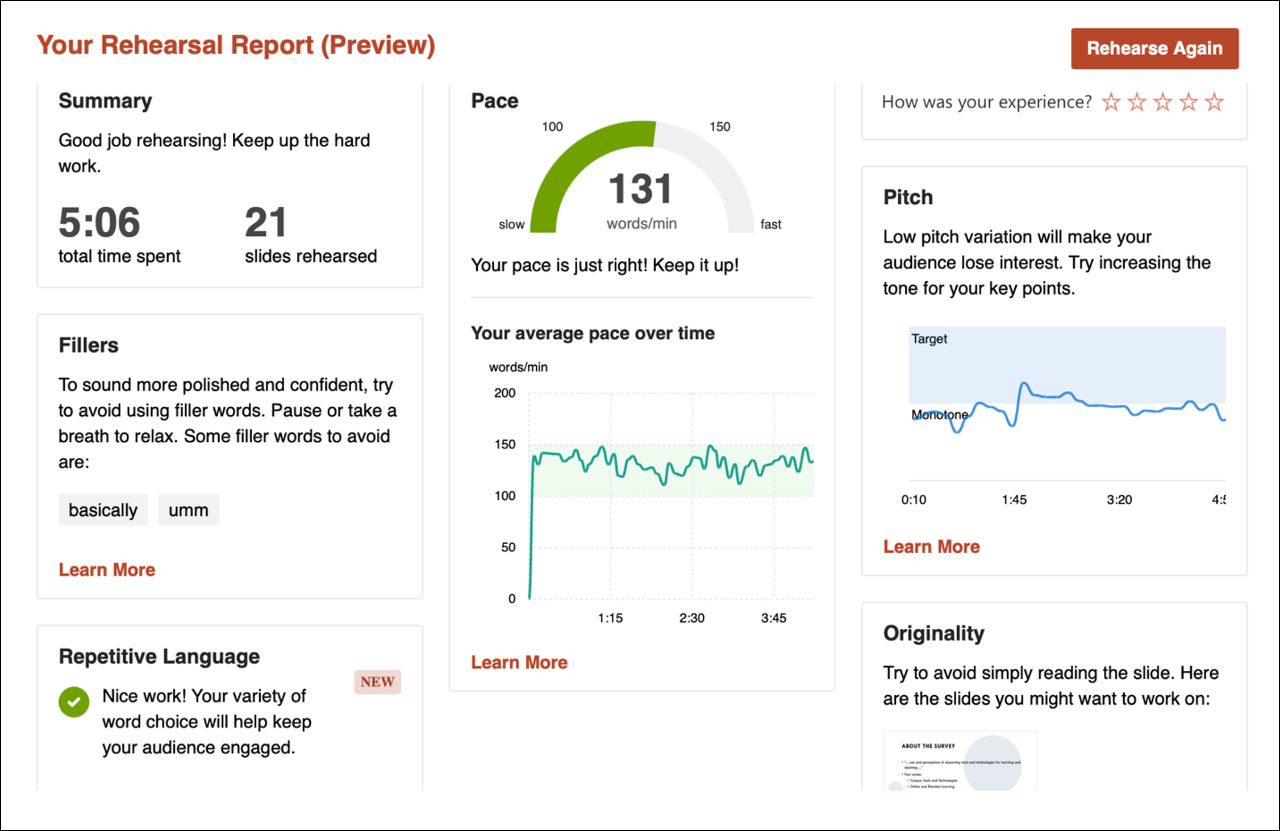
Speaker Coach
This tool, available through PowerPoint, analyzes your presentations as you practice them aloud. At the end of your practice, you receive a rehearsal report, which provides a summary of your presentation, your pace (words per minute), and voice pitch. The analysis reveals filler words (including “umm”) that you used, words you said repetitively, and places where you read directly from the slide.
Visit the Microsoft Speaker Coach website to learn more.
Example of Speaker Coach